Components and Structure of Iron Ore Flotation Machine
The components and structure of an iron ore flotation machine play a crucial role in its efficient operation. Let’s take a closer look at what makes up this important piece of equipment.
The flotation machine consists of a pulp tank where the mixture of water and ground ore is introduced. This tank is equipped with agitators that create turbulence to ensure proper mixing. The turbulent environment allows air bubbles to attach themselves to the valuable minerals present in the ore.

Components and Structure of Iron Ore Flotation Machine
Connected to the pulp tank is a froth removal mechanism, which helps separate the mineral-laden froth from the rest of the slurry. This mechanism typically includes paddles or scrapers that skim off and collect the froth into launder troughs for further processing.
One essential component within an iron ore flotation machine is the rotor-stator arrangement. It comprises rotating blades (the rotor) and stationary vanes (the stator). This design creates shearing forces that help promote bubble-particle collision, aiding in mineral separation.
Additionally, there are various mechanisms for controlling airflow rates, such as adjustable impellers or injectors. These allow operators to optimize conditions based on specific requirements for different types of ores.
Understanding and optimizing these components’ design and function contribute significantly to achieving high-quality concentrate outputs while minimizing operating costs associated with energy consumption and maintenance needs.


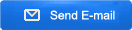
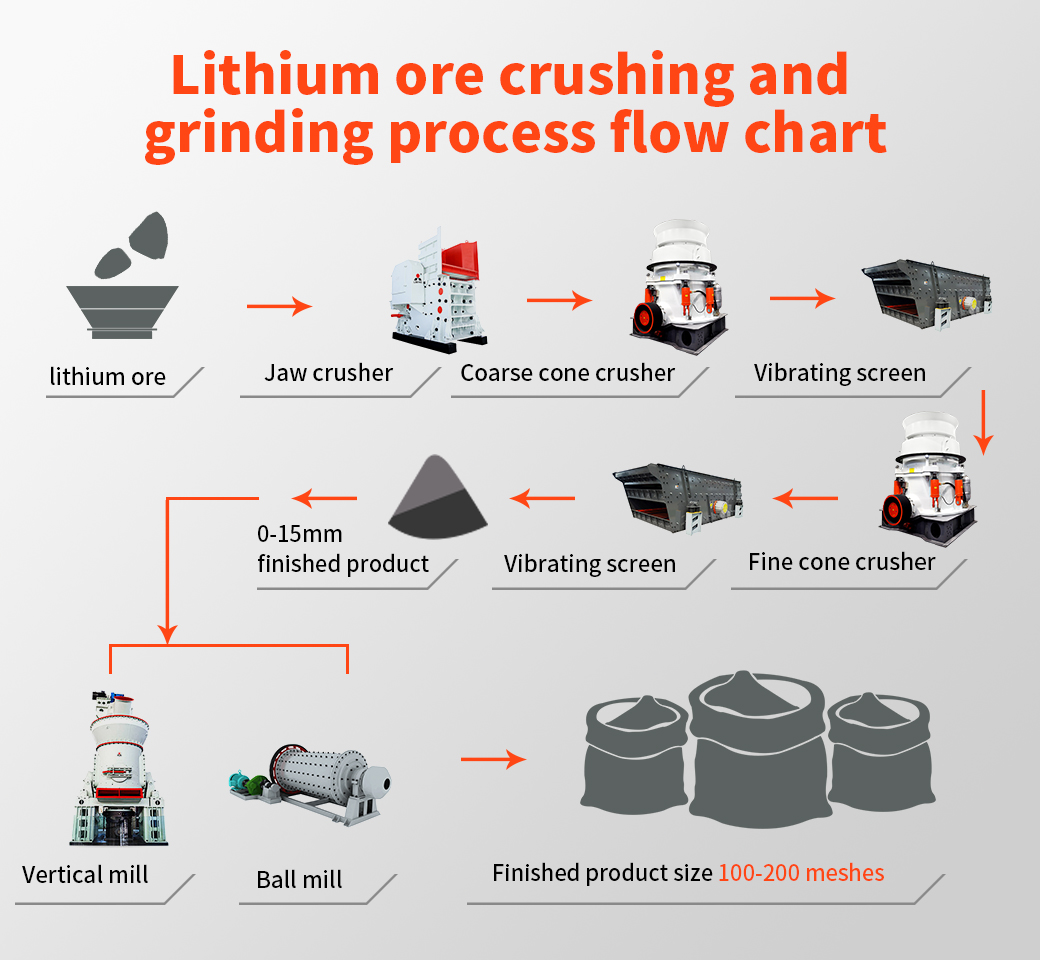 Spodumene: According to the hard rock crushing process, the crushed product is generally 5-40mm, combined with different design requirements of customers, two-end or three-stage crushing, high-grade crushed products (above 4-5%) can be directly used in the metallurgical process to produce lithium carbonate Or lithium hydroxide, the particle size of the finished product is generally around 20-40mm; low-grade generally requires ball mill grinding and separation, and the particle size of the finished product is generally around 5-20mm;
Spodumene: According to the hard rock crushing process, the crushed product is generally 5-40mm, combined with different design requirements of customers, two-end or three-stage crushing, high-grade crushed products (above 4-5%) can be directly used in the metallurgical process to produce lithium carbonate Or lithium hydroxide, the particle size of the finished product is generally around 20-40mm; low-grade generally requires ball mill grinding and separation, and the particle size of the finished product is generally around 5-20mm;